Directory Structure of Linux
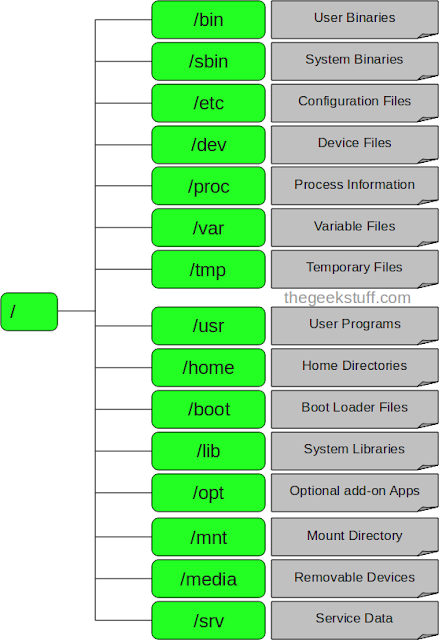
In Linux, the file system is organized in a hierarchical structure, starting from the root directory '/'. All other files and directories are located under the root directory. Some common directories include:
- /bin: Contains binary executables that are used by all users.
- /sbin: Contains binary executables that are used by the system administrator.
- /etc: Contains configuration files for the system and applications.
- /usr: Contains user-related files and programs, such as libraries and documentation.
- /var: Contains variable data, such as log files and mail spools.
- /tmp: Contains temporary files that are deleted when the system is rebooted.
- /home: Contains the home directories for individual users.
This is not an exhaustive list and the directory structure can vary depending on the Linux distribution.





.jpeg)